Authors:
- Alix Tinoco, MD
- Daniel López, MD
- Teresa Urioste, MD
- Edinsson Olate, MD
- Ivo Ferreira, MD
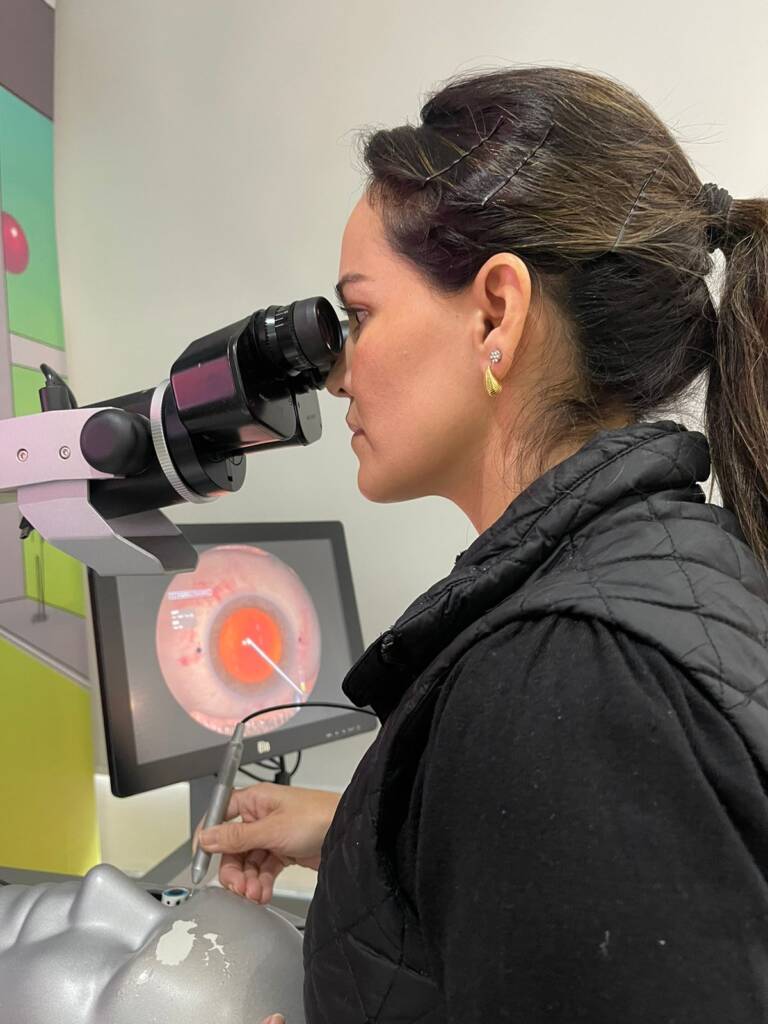
Before embarking on your journey as an eye surgeon, one of the most critical skills to master is the connection between manual control and precision inside the eye. The way a surgeon positions their hands and handles instruments outside the eye directly influences the control and precision needed inside. This transition—from hand movement to instrument navigation in the anterior chamber—demands not only technical skill but also a deep understanding of the anatomy and mechanics of the surgical procedure.
This connection, from macroscopic hand control to microscopic precision within the anterior chamber, is often overlooked in surgical education. Many surgeons enter their careers without fully appreciating how these foundational elements influence outcomes. As studies in microsurgery show, mastering these small, precise movements is essential for achieving high-quality surgical results¹.
Below are six key areas to focus on when developing these essential skills:
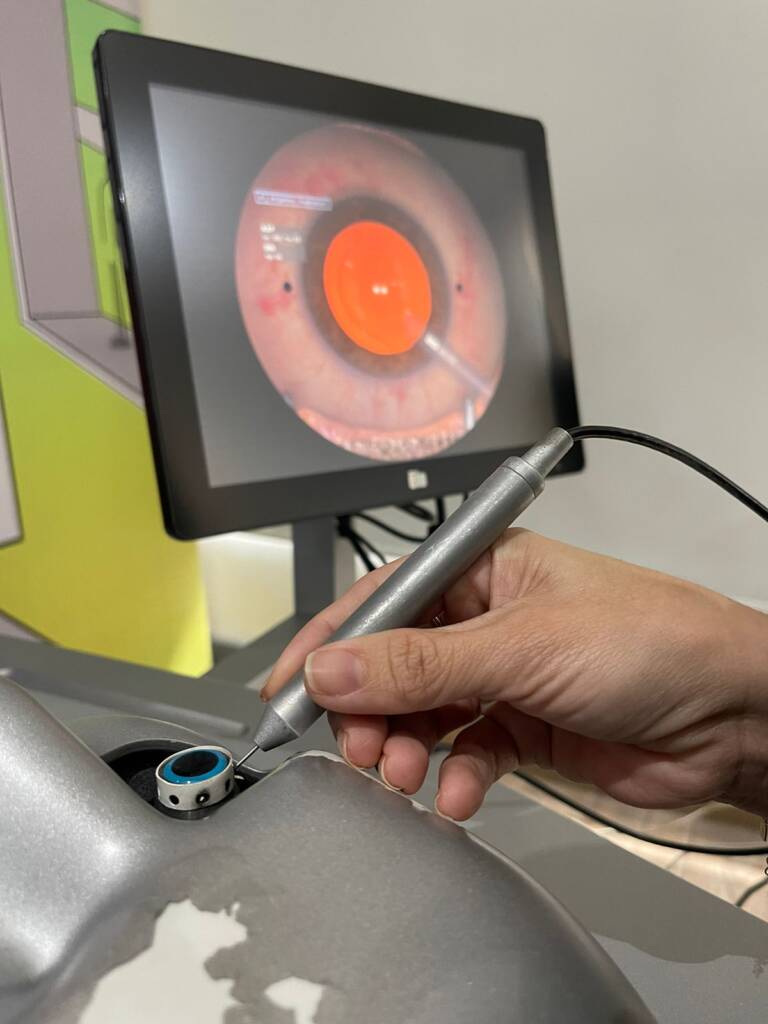
1. Hand Positioning
The position of the hands is critical to maintaining control throughout the surgery. Incorrect hand positioning can lead to tension and fatigue, compromising precision. Proper hand placement minimizes these issues, providing a stable foundation for precise movements.
2. Fixation Points for Tension Release
Creating fixation points with the hand helps release unnecessary tension and promotes steady, controlled movement. This is essential for maintaining precision throughout a procedure that requires continuous focus.
3. Instrument Grip
The way a surgeon holds their instruments is fundamental to achieving a wide range of motion and fine control. Each instrument requires a different approach to grip, and small changes in handling can have a significant impact on precision. For example, phacoemulsification handpieces need to be held differently from second instruments or syringes¹.
4. Biomechanics of Hand Movements
Surgeons must understand the biomechanics of their hand movements. How the hand moves when using different instruments will affect the quality of the surgery. Instruments should be held in a way that allows pivoting within the incision while maintaining control².
5. Incision Navigation
One of the most critical aspects of cataract surgery is how the instrument navigates through the incision. The instrument should “float” through the incision without causing trauma to the surrounding tissue or allowing the escape of essential fluids like viscoelastic. The ability to maintain the integrity of the incision while controlling the movement of the instrument is a key skill³.
6. Precision Navigation in the Anterior Chamber
Inside the eye, precise movements are crucial to avoid damaging delicate structures such as the endothelium (the “roof”) or the posterior capsule (the “floor”). Surgeons must understand the limits of the anterior chamber to ensure they navigate with accuracy and avoid complications. Proper understanding of these anatomical boundaries allows for the best possible outcomes ⁴-².
Conclusion
Mastering manual control and micro precision is fundamental to becoming a skilled cataract surgeon. These skills form the foundation of high-quality eye surgery, allowing surgeons to navigate through small incisions and manipulate instruments with precision inside the delicate environment of the anterior chamber. With proper training and a solid grasp of the biomechanics involved, surgeons can significantly improve their performance and outcomes.
Learn Phaco with Us! Enroll here!
References:
- “Microsurgical Techniques in Ophthalmology: Current Procedures and Functions.” IntechOpen, 2011.
- https://eyesurgeryguide.org/ultrasound-a-key-tool-in-cataract-surgery/
- “Ultrasound ONE TRAY® in Cataract Surgery.” Eye Surgery Guide. 2023
- Haoyu Li, Tanhong Pu, and Liangjing Yang. “Microsurgery Robots: Applications, Design, and Development.” Sensors. 2023
